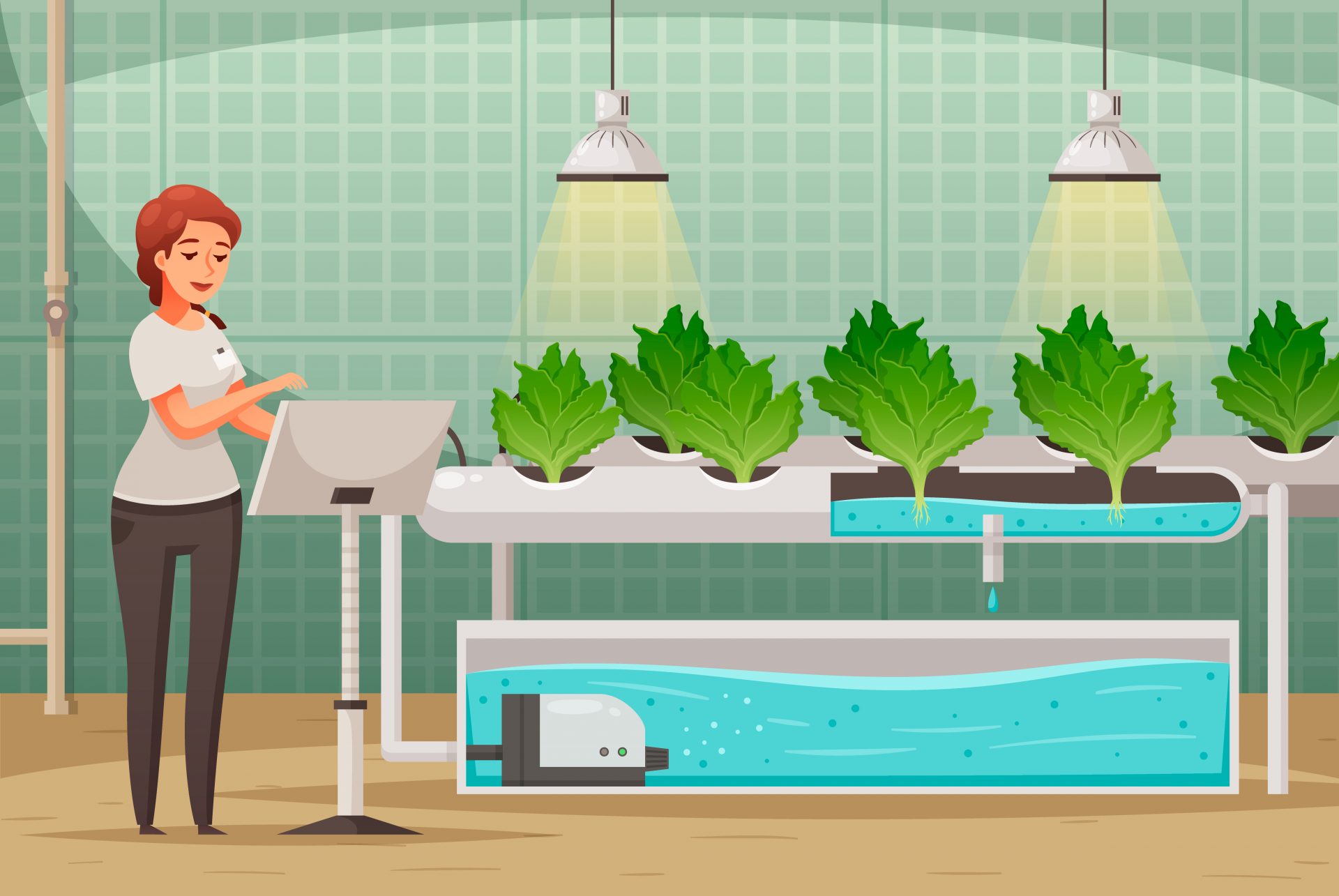
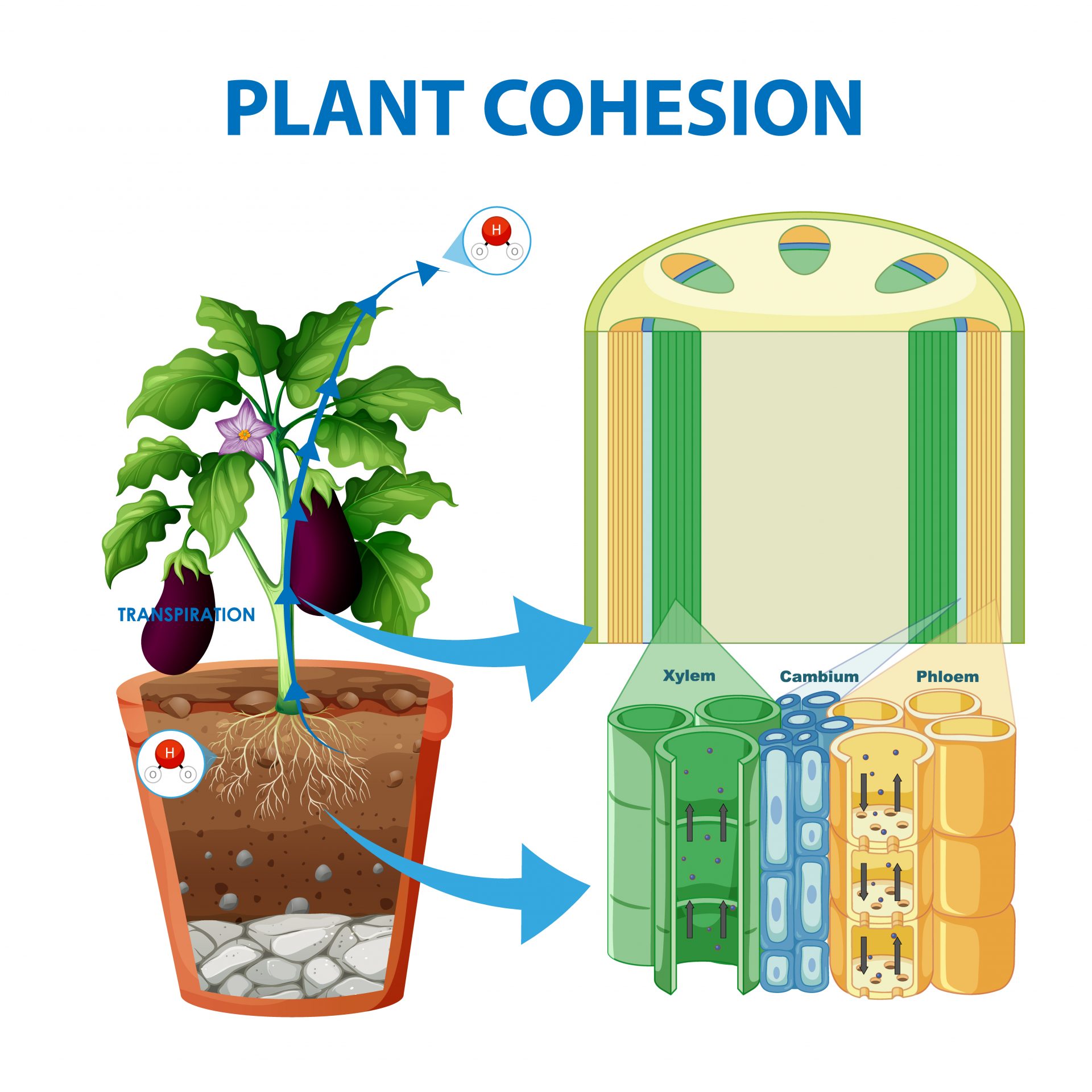
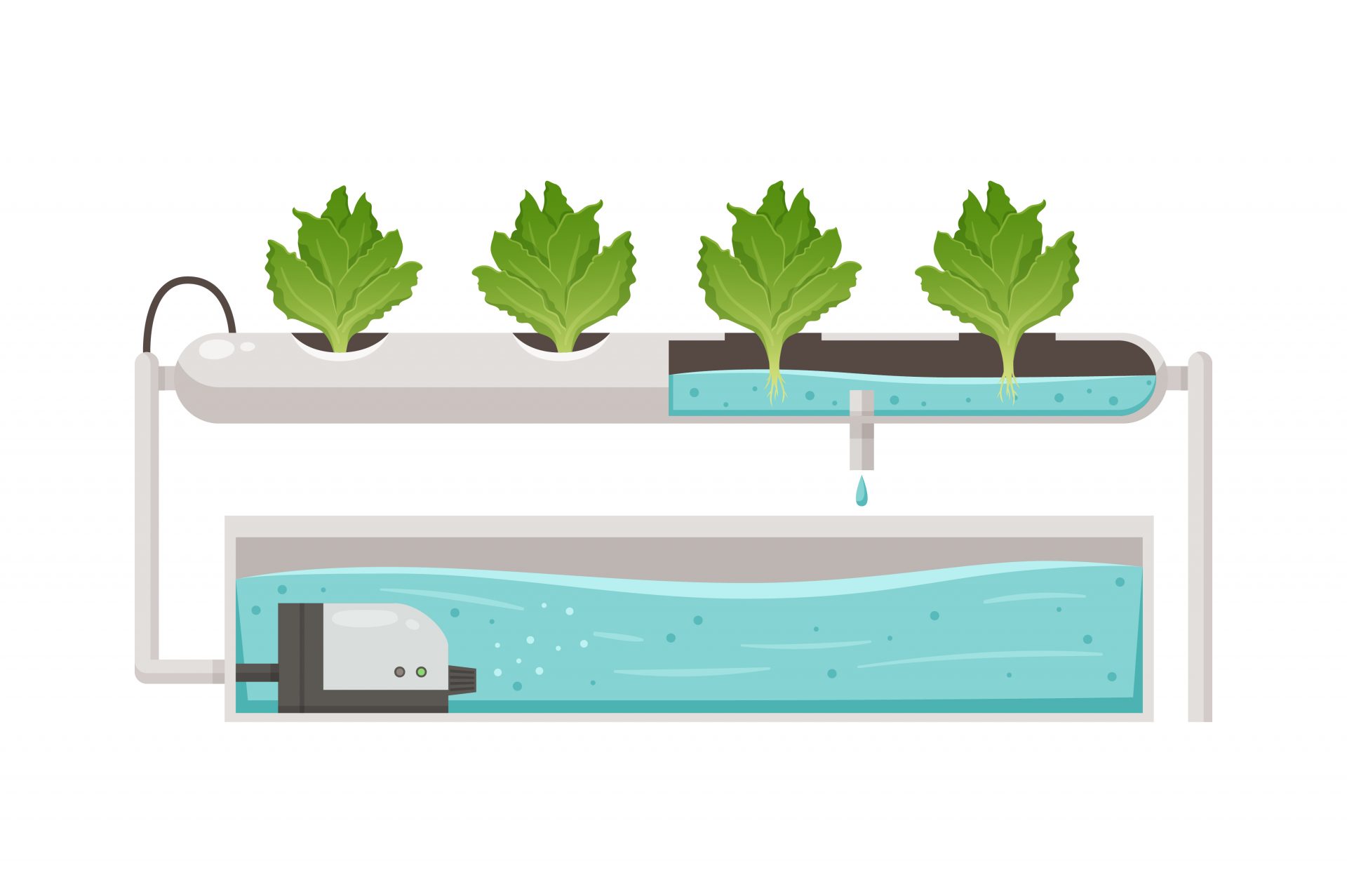
Aquaponic is a revolutionary approach to sustainable agriculture that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil). This symbiotic system has ancient roots, with historical evidence suggesting that the Aztecs and ancient Chinese civilizations practiced similar methods. In the modern context, aquaponics offers a highly efficient, resourcesaving method of food production. As Dr. George Brooks, a leading aquaponics researcher, states, “Aquaponics mimics natural ecosystems to create a balanced, sustainable food production system.
This article delves into the intricate workings of aquaponic fish tank, exploring the principles, components, setup, maintenance, and benefits of this innovative system.
Aquaponic Fish Gardening:Grow your organic plant 10 times more.Hurry up!limited offer
Chapter 1- The Basics of Aquaponics
Aquaponic System Components
Fish Tank
Fish play a crucial role in aquaponics setups as they serve as the natural fertilizer source for plants. Tilapia, trout, catfish, largemouth bass, koi, goldfish, and other ornamental fish are commonly cultivated in these systems. The size of the tank should match the type and number of fish being raised to ensure they have enough space to thrive.
Important considerations when choosing fish for your system include-
- Species compatibility- Opt for fish that thrive in aquaponic environments and are compatible with the chosen plants.
- Temperature adaptability- Ensure the selected fish species can tolerate the system’s climate conditions.
- Growth rate- Maximize productivity by selecting fish with rapid growth rates.
- Nutrient production- Different fish species generate varying amounts of waste, which nourishes the plants. Select species that align with the plants’ nutrient requirements.
- Market demand- Evaluate the commercial viability of the chosen fish species, particularly for commercial aquaponics ventures.
Fish Tank Setup
- Tank Size and Shape- Select a fish tank of suitable size and shape, considering the number and size of fish intended for cultivation. Rectangular or circular tanks are popular choices in aquaponics setups.
- Filtration System- Incorporate a filtration system to eliminate solid waste and uphold water quality. Options encompass mechanical filters, biological filters, and settling tanks.
- Aeration- Ensure sufficient oxygenation of the water using aeration devices like air stones or diffusers. Adequate oxygen levels are crucial for fish health and vitality.
- Temperature Regulation- Maintain the ideal water temperature for the chosen fish species by employing heaters or chillers, depending on prevailing environmental conditions.
- Lighting-Provide adequate illumination for the fish tank, especially if cultivating species that benefit from natural light cycles. LED lights are frequently favored for their energy efficiency and precise control.
Water Quality Management
- Monitoring- Regularly assess water parameters like pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to maintain ideal water conditions for fish and plants.
- pH Adjustment- Keep pH levels stable within the optimal range for the chosen species by using pH buffers or adjusting water alkalinity as necessary.
- Ammonia Detoxification- Utilize biological filtration techniques to convert toxic ammonia from fish waste into less harmful compounds like nitrate through the nitrogen cycle.
- Water Exchange- Periodically exchange water to reduce nutrient buildup and preserve overall water quality, while being cautious not to disrupt the ecosystem balance.
- Disease Prevention- Implement proper hygiene and quarantine procedures to prevent disease transmission among fish. Regularly inspect fish for signs of illness and administer treatment as needed to maintain a healthy population.
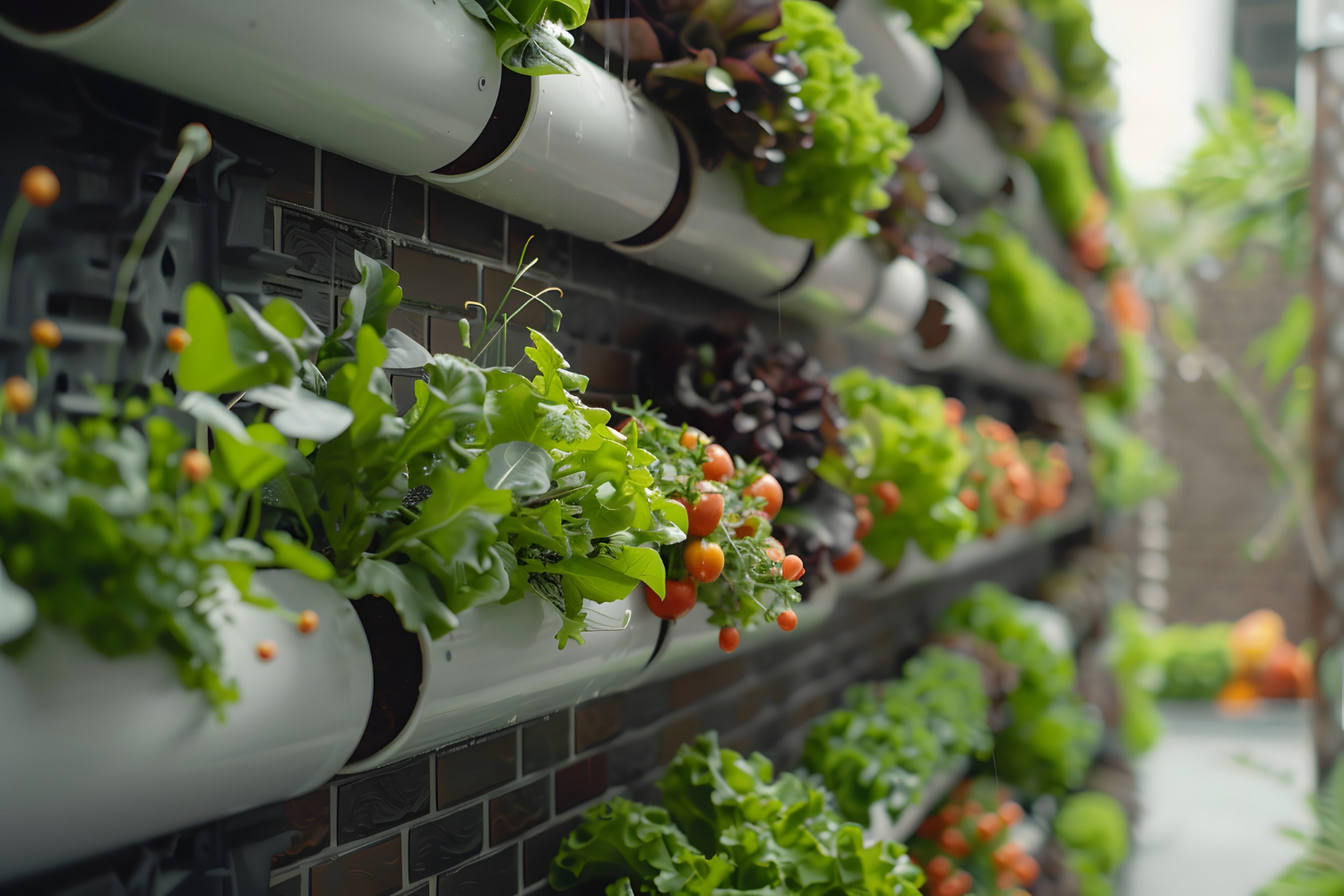
Plant
Choosing the right plants for your aquaponics system is crucial for its success and yield. Here are key considerations
- Species Compatibility- Opt for plant species that thrive in hydroponic environments and can flourish in the nutrientrich water of aquaponics systems.
- Growth Requirements- Consider the light, temperature, and humidity needs of selected plants to ensure optimal growth and productivity.
- Crop Diversity- Enhance system diversity and productivity by selecting a variety of plants with different growth habits and nutrient requirements.
- Edible vs. Ornamental- Determine whether the system’s primary focus is on producing edible crops, ornamental plants, or a combination of both, and choose plant species accordingly.
- Market Demand- Evaluate the market demand and potential profitability of selected plant species, particularly for commercial aquaponics ventures.
Aquaponic System:Buy now at discount of 40%off at $37.Buy Now!!
Construction of Grow Beds
- Bed Material- Opt for suitable materials like foodgrade plastic, wood, or metal to construct the grow beds, ensuring durability, nontoxicity, and resistance to water damage.
- Bed Design- Design the grow beds with adequate depth and surface area to accommodate the root systems of chosen plant species, considering factors like drainage, slope, and ease of maintenance.
- Media Selection- Choose grow media that offer proper support for plant roots while promoting good water retention and aeration, with common options including gravel, expanded clay pellets, and lava rock.
- Irrigation System- Install a dependable irrigation system to deliver water and nutrients to plants, with options ranging from flood and drain systems to drip irrigation or nutrient film technique (NFT) systems.
- Plant Spacing- Determine appropriate spacing based on the mature size and growth habits of selected plants to optimize space usage and prevent overcrowding.
Nutrient Cycling
- Utilization of Fish Waste- Circulate water from the fish tank through grow beds to utilize fish waste as a nutrient source for hydroponic plants, which absorb nutrients and purify water for recirculation.
- Microbial Activity- Foster growth of beneficial bacteria in grow beds, crucial for converting fish waste ammonia into nitrites and nitrates through the nitrogen cycle, providing essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Supplemental Nutrients- Monitor and supplement nutrient levels as necessary to ensure plants receive all essential nutrients like iron, calcium, magnesium, and trace minerals for healthy growth.
- pH Balance- Maintain stable pH levels within the optimal range (typically 5.5 to 7.0) for plant nutrient uptake, adjusting with pH buffers or acids/bases to prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
- Monitoring and Adjustment- Regularly monitor nutrient levels, pH, and overall plant health, making adjustments to optimize nutrient cycling and plant growth as needed.
Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria are vital components of an aquaponics system, contributing to the wellbeing of both fish and plants. They play a critical role in the nitrogen cycle, converting fish waste into nutrients essential for plant growth through a process called nitrification.
Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle
- Ammonia Production- The nitrogen cycle initiates with fish producing ammonia as a waste product through respiration and excretion.
- Nitrosomonas Bacteria- Nitrifying bacteria like Nitrosomonas spp. convert ammonia into nitrites in aerobic conditions, a process known as nitrification.
- Nitrobacter Bacteria- Further nitrification occurs as nitrites are converted into nitrates by additional nitrifying bacteria such as Nitrobacter spp., completing the process.
- Nitrate Uptake by Plants-Plants absorb nitrates from the water through their roots, utilizing them as a nitrogen source for growth and development.
- Denitrification-In certain aquaponics systems, denitrifying bacteria may convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas (N2) under anaerobic conditions, concluding the nitrogen cycle and reducing nitrate accumulation.
Beneficial Bacteria
- Role in Nitrification-Beneficial bacteria are pivotal in the nitrogen cycle, converting toxic ammonia and nitrites from fish waste into less harmful nitrates, which plants readily utilize.
- Importance of Surface Area-Maximizing surface area in grow beds promotes bacterial colonization and efficient nitrification. Porous media like gravel, expanded clay pellets, or biofilter media offer ample surface area for bacterial growth.
- Cycling Process-Beneficial bacteria establish themselves during the initial cycling phase of the aquaponic system, typically lasting several weeks. As fish waste accumulates, providing substrate for bacterial growth, ammonia levels rise. As nitrifying bacteria populations increase, they convert ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates.
- Maintenance-Regular monitoring of water parameters, including ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, is crucial to ensure thriving populations of beneficial bacteria and their vital role in the aquaponic system. Adequate aeration and oxygenation of water also support bacterial growth and activity.
Chapter 2- The Nitrogen Cycle in Aquaponics
Achieving a fully functional and established aquaponics system involves completing the system cycling process, establishing nitrifying bacteria, and ensuring fish show no signs of stress while plants exhibit no nutrient deficiencies. Among the pivotal factors in this process is the presence and regulation of nitrates.
Nitrates serve as a nontoxic form of nitrogen vital for plant cell formation and fish health. However, excessively high nitrate concentrations can lead to uncontrolled plant growth and nitrate accumulation in plant leaves, posing risks to human health. Therefore, it is imperative for aquaponics growers to grasp the significance of nitrates, understand the nitrification process, identify the ideal nitrate levels, and learn how to monitor and adjust these levels in their systems.
Understanding Nitrates
Nitrates represent a less toxic form of nitrogen that serves as a nutrient source for aquaponics plants. While beneficial, excessive nitrates can result in methane gas production, algae proliferation, and elevated acidity levels in the water. Hence, maintaining a balance between fish biomass and the number of plants in the grow bed is crucial to prevent overproduction of nitrates.
The Nitrogen Cycle and Nitrification Process
The nitrogen cycle constitutes a vital biological process in aquaponics, commencing with the introduction of proteinrich fish feed into the system. This feed is broken down by the nitrogen cycle into nitrogen. The subsequent breakdown process involves-
- Ammonia Production-Fish consume the proteinrich feed, excreting it as ammonia into the system.
- Conversion to Nitrites– Nitrifying bacteria like Nitrosomonas convert ammonia into nitrites under aerobic conditions.
- Conversion to Nitrates-Further nitrification occurs as Nitrobacter bacteria convert nitrites into nitrates, completing the process.
The Importance of Nitrates in Aquaponics
Recognizing the significance of nitrates is vital for sustaining continuous cycling essential for fish and plant development. Nitrates serve several key roles in aquaponics systems-
- Essential for fish and plant growth as they constitute key components of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- Formation of nitrates through nitrification aids in reducing the concentration of toxic ammonia excreted by fish.
- Critical for plant growth as nitrogen is a constituent of chlorophyll, playing a pivotal role in photosynthesis.
Ideal Nitrate Levels for Aquaponics
While nitrates are essential, monitoring and maintaining them at optimal levels is crucial to avoid system issues. Although opinions on ideal nitrate levels vary, the most recommended range is between 3 to 150 mg per liter or 150 ppm. While some fish species can tolerate higher levels, adhering to the ideal range helps prevent higher nitrate concentrations in plant leaves.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nitrate Levels
To monitor nitrate levels, aquaponics practitioners can utilize sixinone test strips available online or at local aquaponics stores. Regular monitoring every two to three days is essential, bearing in mind that nitrate levels may initially be low in new systems before bacterial populations develop and increase. Adjustments can be made by-
- Adding more fish or bacteria to address low nitrate levels.
- Adding more plants or reducing fish numbers to mitigate high nitrate levels.
- Conducting partial water changes to lower nitrate levels and restore balance in the system.
Chapter 3- Setting Up an Aquaponic Fish Tank
Setting up an aquaponic fish tank involves creating a symbiotic environment where fish waste fertilizes plants, and the plants filter the water for the fish. By combining aquaculture and hydroponics, this sustainable system minimizes waste while yielding fresh produce and healthy fish. Considerations before Embarking on an Aquaponics System Journey
Personal Factors
- Selecting the Right System– Determine the type of aquaponics system that aligns with your preferences and objectives, whether it’s mediabased, raftbased, NFT (Nutrient Film Technique), or a blend of these methods.
- Purpose and Goals– Define the purpose of your aquaponics venture. Identify the specific plants and fish you aim to cultivate and whether they are intended for personal consumption. This clarity is crucial for tailoring your system to meet your goals effectively.
- DIY Inclination- Assess your inclination towards DIY projects versus purchasing a preassembled system. While constructing your own system can be a gratifying learning process despite the trial and error, opting for a premade system offers the advantage of quick setup with technical support.
Environmental Factors
- Humidity Management- Given the constant water flow in aquaponics, anticipate natural evaporation and heightened moisture levels in your space.
- Water Containment- Be mindful of potential water spillage from the fish tank or grow beds, necessitating a location tolerant to moisture.
- Lighting Requirements- Plants thrive on light for photosynthesis. While sunlight is optimal, indoor systems may require supplementary grow lights. Choose lighting solutions carefully, considering the light spectrum plants absorb.
Location and Space Considerations
- Sunlight Access- Ensure the chosen location provides adequate natural light exposure, essential for plant growth.
- Temperature Regulation- Opt for a location where temperature control is feasible, possibly requiring the installation of heaters or air conditioners for consistency.
- Water Accessibility- Proximity to a reliable water source is vital for sustaining the aquaponic system’s water supply. Adequate drainage to prevent water accumulation is also necessary.
- Electrical Proximity- Consider the availability of electrical outlets for powering water and air pumps. Utilizing extension cords may be necessary to reach nearby outlets.
- Ventilation Needs- Proper airflow and ventilation are crucial to prevent humidity buildup and maintain optimal conditions for both plants and fish.
Chapter 5- Maintenance and Management
Essential Water Quality Maintenance Tasks
Nurturing your aquaponic ecosystem requires diligent upkeep to ensure its vitality. Key tasks include-
- pH Monitoring Regularly assess pH levels to support optimal conditions for both fish and plants, as fluctuations can impact nutrient absorption.
- Ammonia and Nitrite Levels Keep a close eye on these levels to maintain a healthy nitrogen cycle, preventing stress on fish and hindrances to plant growth.
- Nitrate Levels Monitor nitrate concentrations to strike a balance that fosters plant growth without risking overaccumulation.
Ensuring Fish Health and Balanced Feeding
Prioritize the wellbeing of your aquatic inhabitants with these practices-
- Regular Observation– Monitor fish behavior for signs of stress or illness, intervening early to mitigate potential issues.
- Controlled Feeding– Establish a feeding schedule to provide adequate nutrition without overloading the system with excess waste.
- Dietary Diversity– Offer varied diets to promote fish health, incorporating highquality food for a balanced nutritional intake.
Plant Pruning and Pest Management
Promote plant health and safeguard against pests with these measures-
- Pruning– Trim plants regularly to encourage healthy growth and prevent overcrowding, maintaining ecosystem equilibrium.
- Pest Control– Stay vigilant for signs of pests, addressing them promptly with natural remedies to uphold system integrity.
Troubleshooting Aquaponics Challenges
While managing an aquaponics setup, encountering occasional issues is normal. Address common challenges with the following strategies-
- Imbalanced Nutrient Levels– Adjust feeding and water changes based on water parameter tests to restore equilibrium for optimal growth.
- Fish Health Concerns– Quarantine new fish and monitor existing ones for signs of illness, taking preventive measures to safeguard their health.
- PlantRelated Issues– Address nutrient imbalances promptly to support robust plant growth, tailoring care as needed.
Aquaponic System:Buy now at discount of 40%off at $37.Buy Now!!
Chapter 6- Benefits and Challenges of Aquaponic Fish Tanks
1. Environmental Advantages of Aquaponics
- Water Efficiency: Aquaponics significantly reduces water usage compared to traditional farming methods by employing a closed-loop system that recirculates water between fish tanks and grow beds, minimizing waste.
- Chemical-Free Cultivation: Eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, aquaponics relies on natural fish waste to nourish plants, resulting in chemical-free produce that is safer for both consumers and the environment.
- Space Optimization: Unlike traditional farming, aquaponics requires minimal land, making it ideal for urban settings and reducing habitat destruction associated with large-scale agriculture.
2.Economic Benefits of Aquaponics
- Enhanced Productivity: Aquaponics yields higher crop and fish yields in less time due to optimal growing conditions, offering a lucrative alternative to conventional farming.
- Cost Savings: With reduced water usage, elimination of chemical inputs, and minimal land requirements, aquaponics leads to significant production cost savings.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Beyond crop and fish sales, aquaponics provides income opportunities through value-added products, educational workshops, and consulting services.
3.Health Benefits of Aquaponics
- Chemical-Free Produce: Aquaponically grown produce is free from harmful chemicals, promoting better health and reducing exposure to contaminants.
- Nutrient-Rich Harvest: Plants cultivated in aquaponic systems are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, offering fresher and more nutritious options for consumers.
- Food Security: Aquaponics ensures a consistent supply of fresh produce year-round, enhancing food security and accessibility.
4.Educational and Social Impact of Aquaponics
- Hands-On Learning: Aquaponics provides practical education opportunities for schools and communities, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and career development.
- Environmental Awareness: By promoting sustainable agriculture practices, aquaponics raises awareness about environmental stewardship and inspires innovation.
- Community Engagement: Aquaponics strengthens local food systems, reduces carbon footprints, and improves food access, fostering community resilience and social cohesion.
Challenges and Considerations
- Maintenance Complexity: Water quality management, pest control, system upkeep, and fish health require consistent attention and expertise.
- Initial Setup Costs: Infrastructure, water quality monitoring equipment, fish, and plant stock, and energy expenses contribute to the initial investment.
- Species Selection: Choosing suitable fish and plants, planning crop rotation, and optimizing resource utilization are critical for system success.
Aquaponic System:Buy now at discount of 40%off at $37.Buy Now!!
Conclusion
In conclusion, aquaponics represents a groundbreaking approach to sustainable agriculture, intertwining aquaculture and hydroponics to create a harmonious ecosystem where fish and plants thrive together. With its roots dating back to ancient civilizations, aquaponics has evolved into a modern solution for efficient, resource-saving food production.
As Dr. George Brooks aptly puts it, aquaponics mimics natural ecosystems, fostering a balanced and sustainable food production system. This article has delved into the intricacies of aquaponic fish tanks, covering everything from system components and setup to maintenance and benefits.
By harnessing the power of fish waste to nourish plants and vice versa, aquaponics offers numerous environmental, economic, health, educational, and social advantages. From reduced water usage and chemical-free cultivation to enhanced productivity and community engagement, aquaponics stands as a beacon of innovation in the realm of agriculture.
Aquaponic System:Buy now at discount of 40%off at $37.Buy Now!!